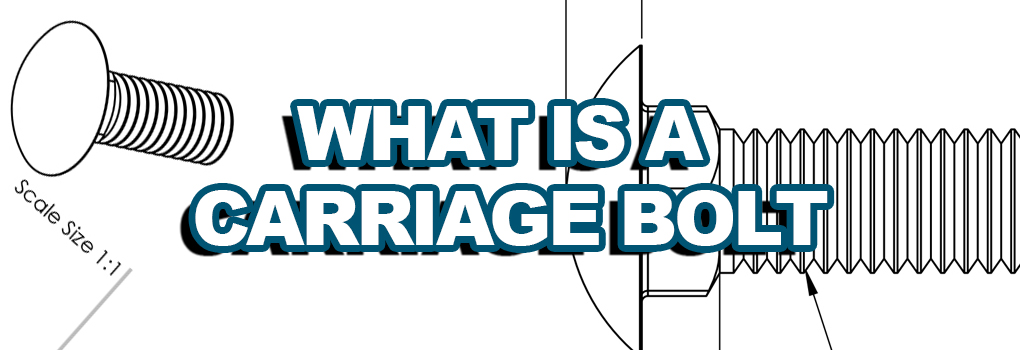
What Is A Carriage Bolt
Carriage bolts have a mushroom-shaped head and a fused square nut underneath the head. The head is usually shallow and dome-shaped. The squared section has a plain unthreaded shank and is of the same size as the bolt shank’s diameter.
Where do carriage bolts get their name?
In the early 1800s, they became popular because they were widely used in the construction of carriages and carriage wheels, thus being christened carriage bolts.
What are carriage bolts used for?
Carriage bolts are used to hold together wood with wood, wood with metal, and even metal with metal. Their particular shape allows the bolt to be self-locking when placed through a square hole, especially when dealing with metal. Alternatively, it can also be easily placed through a round hole in most kinds of wood, making it a versatile accessory.
What are the modern applications of carriage bolts?
The most common modern applications of carriage bolts are carpentry and wood construction. They are frequently used by homeowners, and also by professional carpenters, for DIY projects, home maintenance, and repairs.
Why use carriage bolts?
Carriage bolts are commonly used because of their ease of use, especially when dealing with wood. Their smooth, dome-shaped heads offer an aesthetic appeal and some amount of safety when used in building wooden decking, decorative fencing, wooden furniture, and backyard play equipment. Along with safety, carriage bolts also provide security as they can only be unbolted from one side. They can be used in fixing doors to prevent unscrewing from the wrong side.
How much weight can a carriage bolt hold?
Carriage bolts are easily installed and usually need a single tool for the operation. Having said that, once installed, they can hold large amounts of weight. For example, a Grade 5 carriage bolt made out of carbon steel has a tensile strength of 120,000psi or 8437 kilogram-force per square meter and a proof load strength of 85,000psi or 5,976 kilogram-force per square meter.